jstack 指令
1.线上linux性能排查
查内存
free -m
查负载 M按内存排序,top 然后P按使用率排序。或者
top -c
查磁盘
df -h
2.得到负载最高的进程PID
使用命令查看子线程负载情况,查看进程数 ps -eLf | grep PID | wc -l
top -Hp PID
获取线程最高负载的线程pid,转化为16进制 xxxx,对应堆栈打印的应该就是tid=0x00xx
printf "%x\n" pid
00xx
3.使用jstack查看堆栈信息
打印对应堆栈信息关键字后20行,-l表示打印额外的锁信息。BLOCKED 死锁关键字。
jstack -l pid | grep '00xx' -A 20 >> dump
4.查看子线程数目
-L显示具体的子线程信息,配合wc -l命令查看子线程数目可以很直观的看到效果。一般暴增子线程数都是线上的批量操作操作资源没有关闭导致的。
ps -eLf|grep pid
也可以 其中Threads后面跟的就是线程数
cat /proc/PID/status
5.查看内存信息
ps p PID -L -o pcpu,pmem,pid,tid,time,tname,cmd
jmap 命令
[root@-81]# jmap
Usage:
jmap [option] <pid>
(to connect to running process)
jmap [option] <executable <core>
(to connect to a core file)
jmap [option] [server_id@]<remote server IP or hostname>
(to connect to remote debug server)
where <option> is one of:
<none> to print same info as Solaris pmap
-heap to print java heap summary
-histo[:live] to print histogram of java object heap; if the "live"
suboption is specified, only count live objects
-clstats to print class loader statistics
-finalizerinfo to print information on objects awaiting finalization
-dump:<dump-options> to dump java heap in hprof binary format
dump-options:
live dump only live objects; if not specified,
all objects in the heap are dumped.
format=b binary format
file=<file> dump heap to <file>
Example: jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=heap.bin <pid>
-F force. Use with -dump:<dump-options> <pid> or -histo
to force a heap dump or histogram when <pid> does not
respond. The "live" suboption is not supported
in this mode.
-h | -help to print this help message
-J<flag> to pass <flag> directly to the runtime system
导出 dump 文件:
jmap -dump:live,file=dump.bin,format=b 9667
查看堆 heap 的情况
jmap -heap 9667
打印 jvm heap 的直方图。其输出信息包括类名,对象数量,对象占用大小。
[root@-81 data2]# jmap -histo:live 9667 |head -n 10
num #instances #bytes class name
----------------------------------------------
1: 8924 175292816 [B
2: 144536 20573344 [C
3: 420675 13461600 com.elasticsearch.analyzer.cnsegmet.PreFixTree$TreeNode
4: 420676 9094392 [Lcom.elasticsearch.analyzer.cnsegmet.PreFixTree$TreeNode;
5: 35315 5387808 [Ljava.lang.Object;
6: 49435 4350280 java.lang.reflect.Method
7: 110358 3531456 java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap$Node
jstat 命令
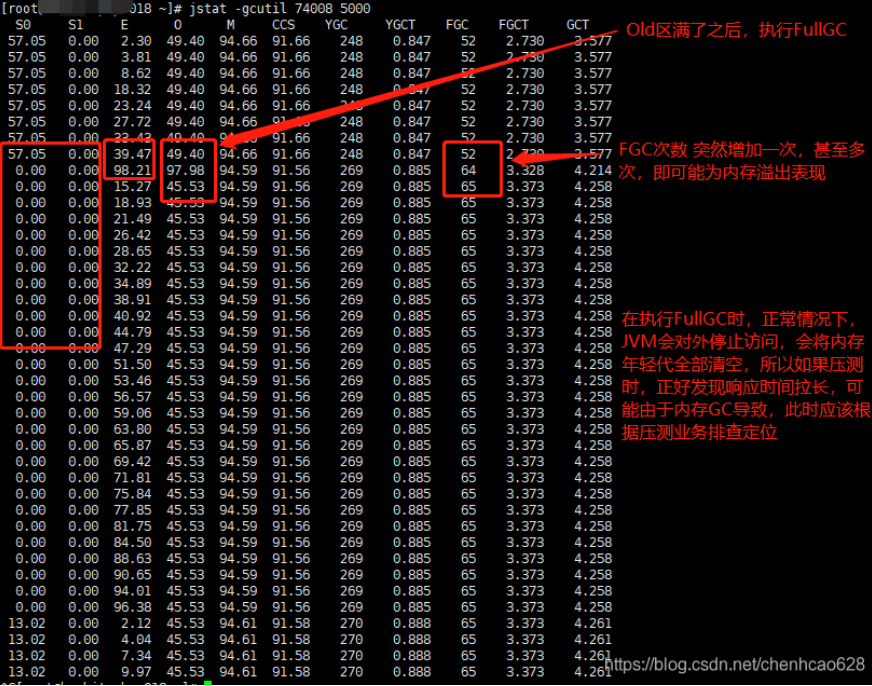
jstat -gcutil PID 1000 表示每隔1s执行一次
[ivory@gaivory root]$ jstat -gcutil 3178 2000
S0 S1 E O M CCS YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT
4.05 0.00 11.93 31.60 96.07 93.17 146 1.659 6 0.079 1.737
4.05 0.00 11.94 31.60 96.07 93.17 146 1.659 6 0.079 1.737
4.05 0.00 12.02 31.60 96.07 93.17 146 1.659 6 0.079 1.737
4.05 0.00 12.03 31.60 96.07 93.17 146 1.659 6 0.079 1.737
- S0 Heap上的 Survivor space 0 区已使用空间的百分比
- S1 Heap上的 Survivor space 1 区已使用空间的百分比
- E Heap上的 Eden space 区已使用空间的百分比
- O Heap上的 Old space 区已使用空间的百分比
- M 元数据区使用比例
- YGC 从应用程序启动到采样时发生 Young GC 的次数
- YGCT Young GC 总时间
- FGC 从应用程序启动到采样时发生 Full GC 的次数
- FGCT Full GC 总时间
- GCT GC总时间
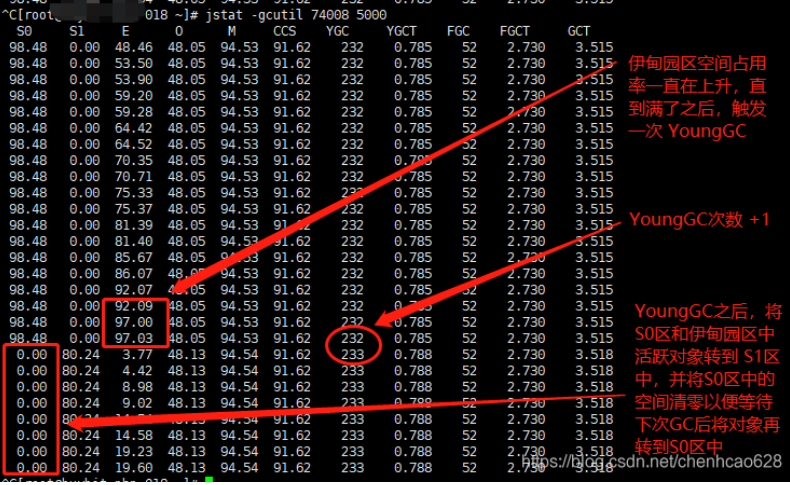
YGC 理解
新生代内存按照 8:1:1 的比例分为一个 eden 区和两个 survivor(survivor0, survivor1) 区。一个Eden区,两个 Survivor区。新 new 出来的对象会存储在 Eden(伊甸园)中,当这区域满了之后JVM会进行一次垃圾回收,在回收时把有用的对象存储在 S1 区,没用的就销毁此对象的内存空间,这过程即第一次 YoungGC,如果 S1 区空间也满了后,同理会将有用的对象会放到 S2 区中,并释放 S1 空间,以上反复的回收即为 YoungGC。
FULL GC 理解
年轻代空间满了之后,会将满足一定活跃度的对象放到 Old 区中(对象活跃度:每个对象满足JVM默认 count=15 之后就判断是活跃对象,每次 YoungGC 后会将存活对象生命中 +1,直到 =15 就转到 Old 区,这个次数可以通过:-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold 来配置), 由于 Full GC 需要对整个堆进行回收,导致应用访问变慢,因此应该尽可能减少Full GC 的次数。